Ensuring Safety In Fuel Transfer Systems: Connector Design Insights
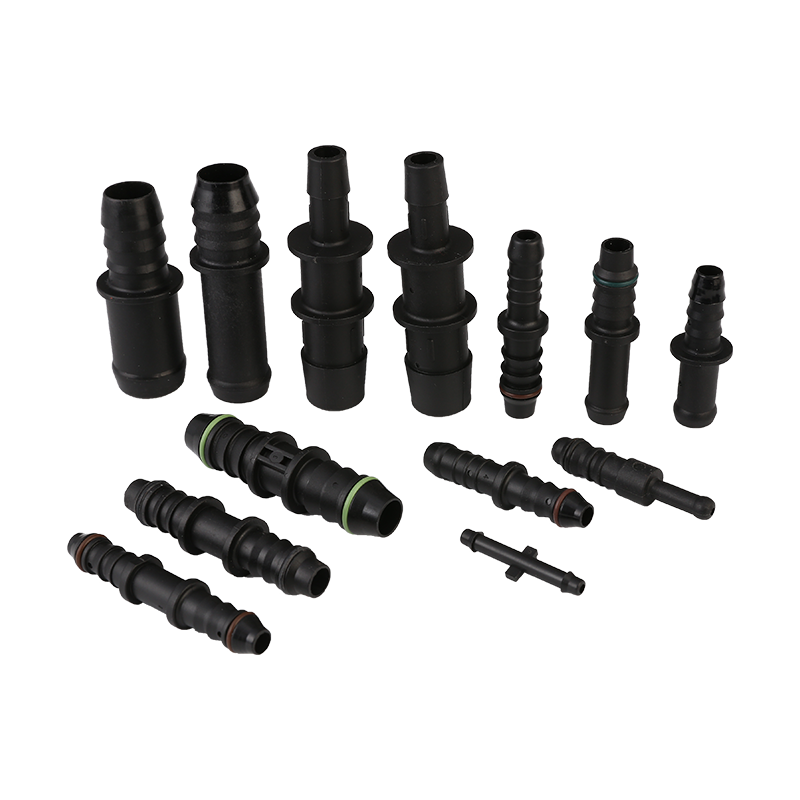
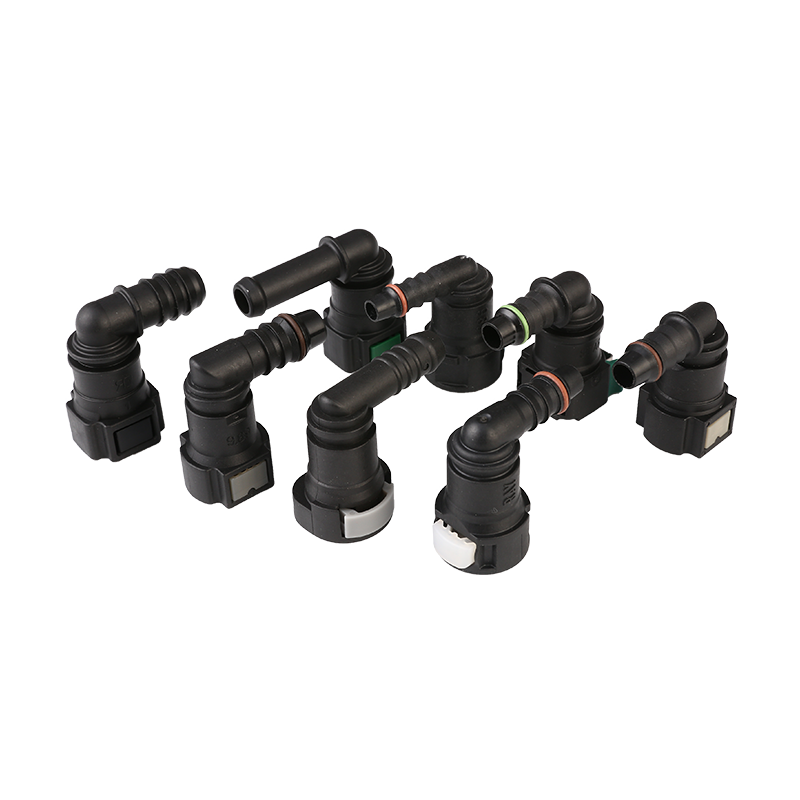
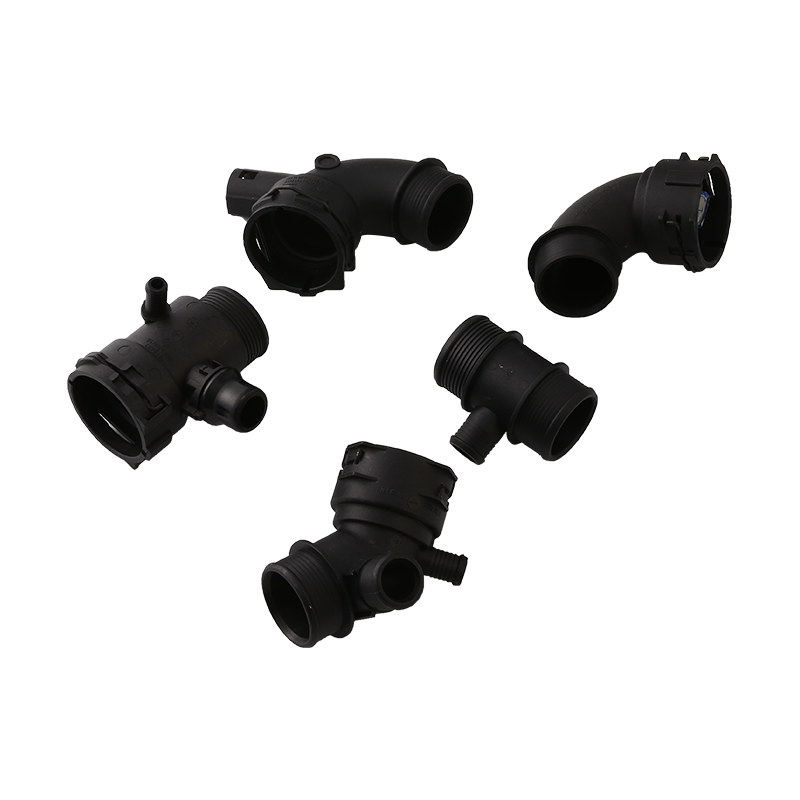
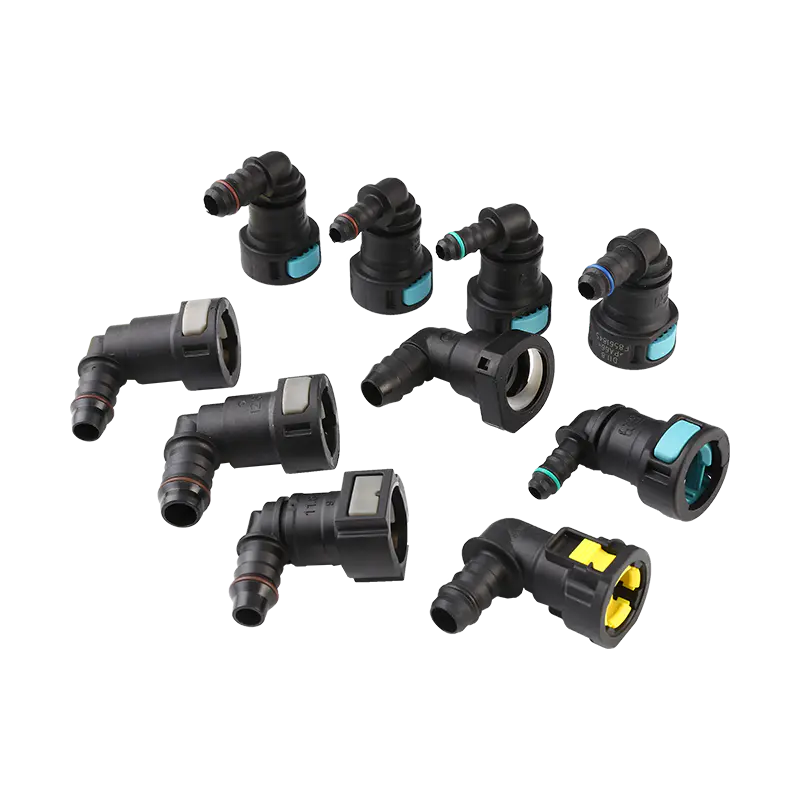
Fuel transfer systems play a crucial role in automotive and industrial applications, where secure and efficient fuel delivery is essential. Among the key components that ensure reliability are Car Fuel Pipe Connectors and Fuel Quick Connectors. These parts must meet strict safety standards to prevent leaks, spills, and potential hazards.
The Importance of Secure Fuel Connectors
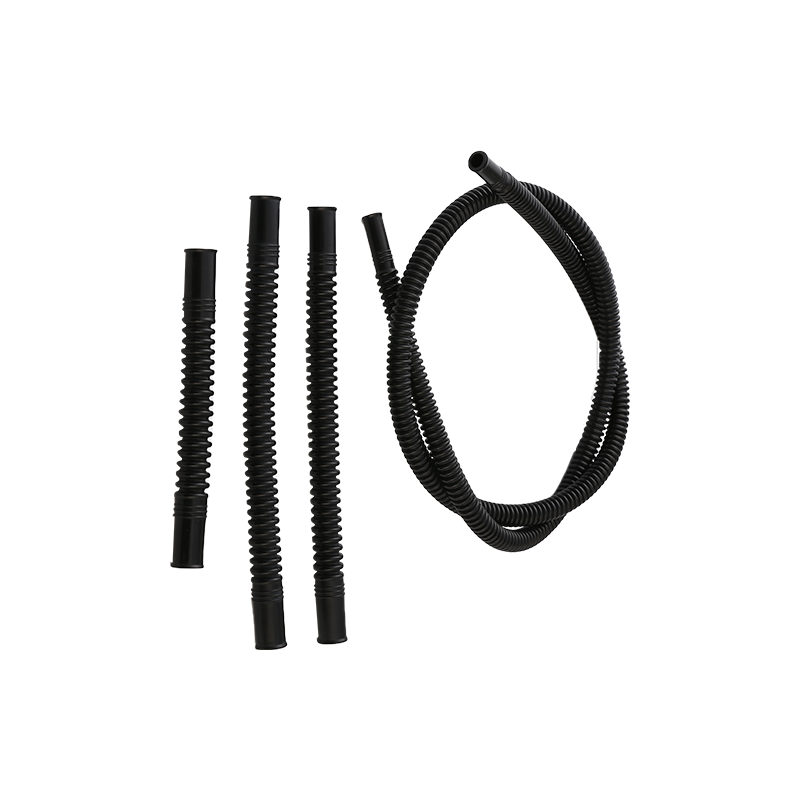
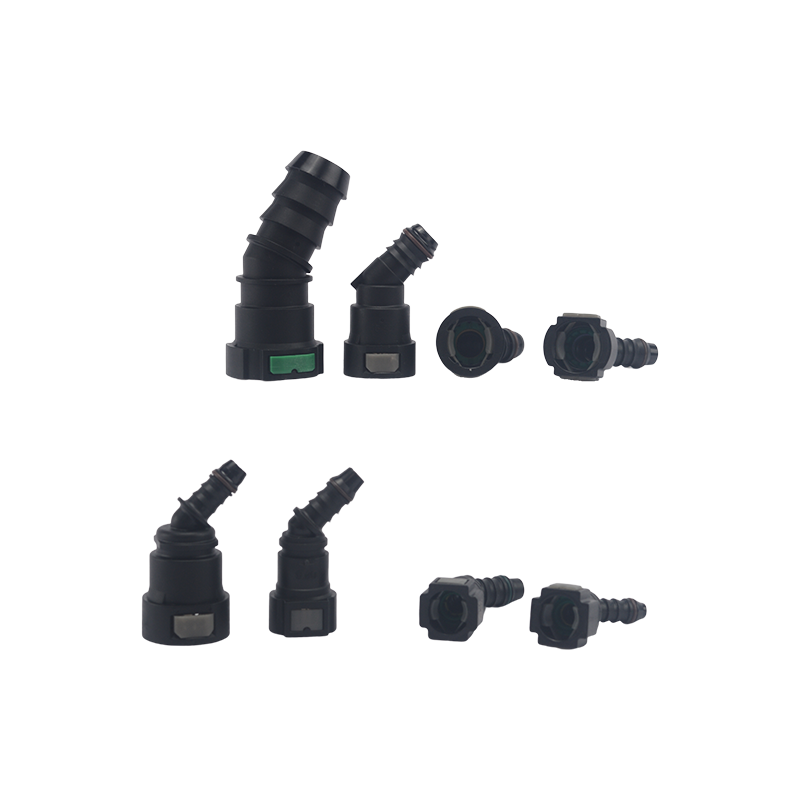
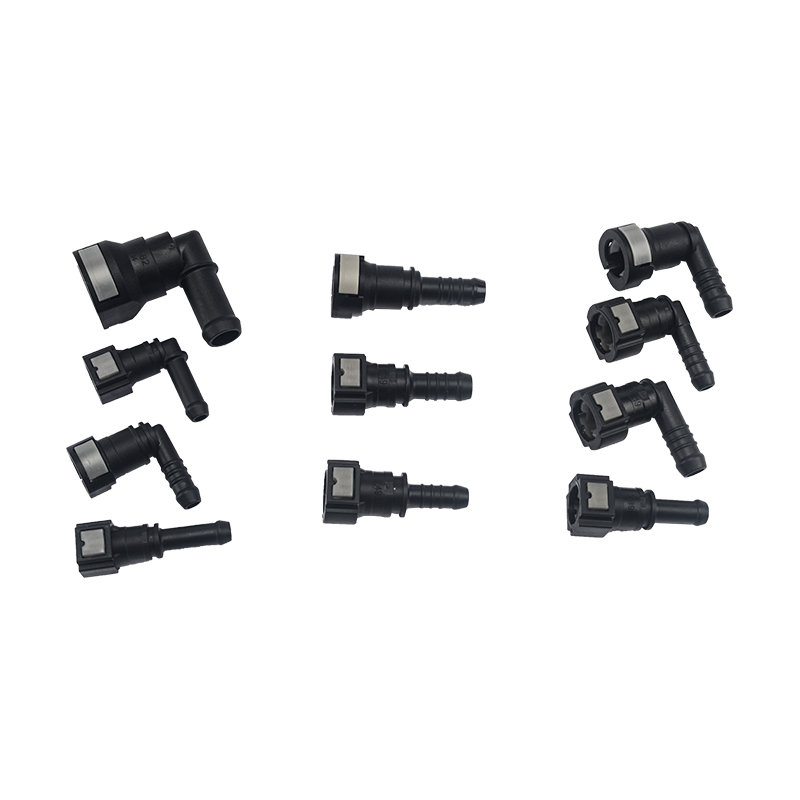
Fuel systems rely on precision-engineered connectors to maintain a sealed flow of gasoline, diesel, or other fuels. Car Fuel Pipe Connectors are designed to withstand pressure variations, temperature changes, and chemical exposure, ensuring long-term durability. Similarly, Fuel Quick Connectors provide fast and secure connections, often used in applications requiring frequent assembly and disassembly.
A poorly designed connector can cause fuel leaks, which pose fire risks and environmental hazards. Therefore, manufacturers prioritize robust materials, leak-proof sealing mechanisms, and corrosion resistance in their designs.
Key Design Considerations for Fuel Connectors
1. Material Selection
The choice of materials significantly impacts connector performance. More Car Fuel Pipe Connectors use high-grade thermoplastics, nylon, or stainless steel, which resist fuel degradation and corrosion. Fuel Quick Connectors often incorporate reinforced polymers or metal alloys to endure mechanical stress and chemical exposure.
2. Sealing Mechanisms
A secure seal prevents fuel leakage, even under pressure fluctuations. Common sealing methods include:
O-Rings – Made from fuel-resistant elastomers like FKM (fluoroelastomer) for tight sealing.
Threaded or Push-to-Connect Designs – Ensures a firm hold while allowing easy installation.
Double-Locking Systems – Some Fuel Quick Connectors feature secondary locks for added safety.
3. Pressure and Temperature Resistance
Fuel systems operate under varying pressures and temperatures. Connectors must maintain integrity in hard conditions, whether in high-performance engines or industrial fuel transfer setups.
4. Ease of Installation and Maintenance
Quick-connect designs in Fuel Quick Connectors reduce assembly time while ensuring a secure fit. Meanwhile, Car Fuel Pipe Connectors often feature ergonomic designs for hassle-free maintenance.
Common Challenges and Solutions
1. Fuel Leakage Risks
Leaks often occur due to worn-out seals or improper installation. Regular inspection of Car Fuel Pipe Connectors and replacing damaged O-rings can prevent this issue.
2. Chemical Degradation
Certain fuels contain additives that may degrade low-quality plastics. Using chemically resistant materials in Fuel Quick Connectors ensures longevity.
3. Vibration and Mechanical Stress
Vehicles and machinery generate vibrations that can loosen connectors. Locking mechanisms in Fuel Quick Connectors help maintain a secure connection even in high-vibration environments.
Good Practices for Safe Fuel Transfer Systems
To maximize safety and efficiency, follow these guidelines:
Regular Inspections – Check Car Fuel Pipe Connectors for cracks, wear, or leaks.
Use Compatible Materials – Ensure connectors match the fuel type and operating conditions.
Follow Manufacturer Guidelines – Proper installation prevents premature failure.
Avoid Over-Tightening – Excessive force can damage threads or seals in Fuel Quick Connectors.
Replace Aging Components – Proactively swap out worn connectors to prevent failures.
The reliability of fuel transfer systems depends heavily on well-designed Car Fuel Pipe Connectors and Fuel Quick Connectors. By focusing on material durability, sealing efficiency, and ease of maintenance, manufacturers can enhance safety and performance. Whether in automotive or industrial applications, selecting the right connectors and adhering to good maintenance practices ensures leak-free operation and long-term system integrity.
Investing in high-quality fuel connectors not only less risks but also optimizes fuel delivery efficiency, making them a critical component in any fuel-dependent system.

 English
English
 Español
Español